Frontiers in Oncology , 19 June 2023
Lestaurtinib inhibits Citron kinase activity and medulloblastoma growth through induction of DNA damage, apoptosis and cytokinesis failure
Pallavicini G 1,2 *, Iegiani G 1,2 *, Parolisi R 1,2 , Ferraro A 1,2 , Garello F 3 , Bitonto V 3 , Terreno E 3 , Gai M 3 and Di Cunto F 1,2
Introduction
Medulloblastoma (MB), the most common malignant pediatric brain tumor, is currently treated with surgery followed by radiation and chemotherapy, which is accompanied by severe side effects, raising the need for innovative therapies. Disruption of the microcephaly-related gene Citron kinase (CITK) impairs the expansion of xenograft models as well as spontaneous MB arising in transgenic mice. No specific CITK inhibitors are available.
Methods
Lestaurtinib, a Staurosporine derivative also known as CEP-701, inhibits CITK with IC50 of 90 nM. We therefore tested the biological effects of this molecule on different MB cell lines, as well as in vivo, injecting the drug in MBs arising in SmoA1 transgenic mice.
Results
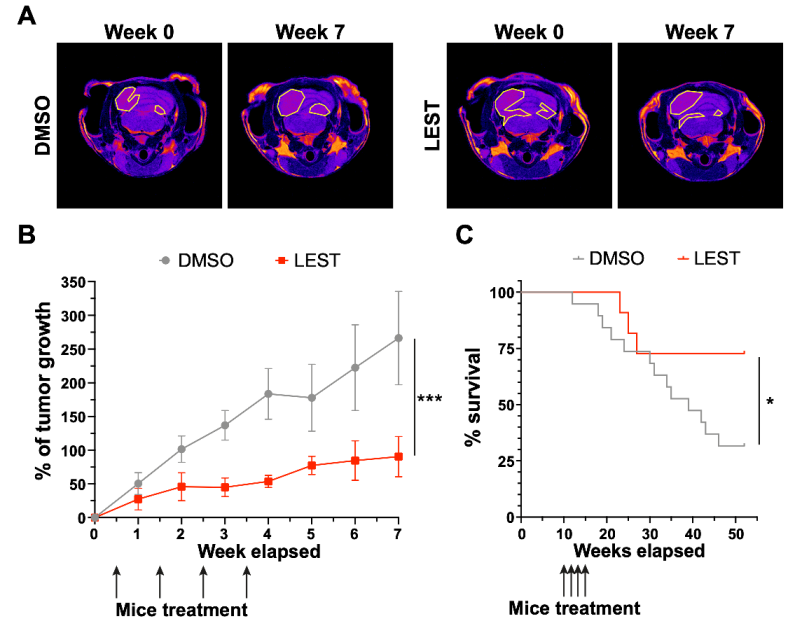
Similar to CITK knockdown, treatment of MB cells with 100 nM Lestaurtinib reduces phospho-INCENP levels at the midbody and leads to late cytokinesis failure. Moreover, Lestaurtinib impairs cell proliferation through CITK-sensitive mechanisms. These phenotypes are accompanied by accumulation of DNA double strand breaks, cell cycle block and TP53 superfamily activation in vitro and in vivo. Lestaurtinib treatment reduces tumor growth and increases mice survival.
Discussion
Our data indicate that Lestaurtinib produces in MB cells poly-pharmacological effects extending beyond the inhibition of its validated targets, supporting the possibility of repositioning this drug for MB treatment.
Lestaurtinib inhibits medulloblastoma progression in SmoA1 mice (A) Representative T2 weighted MRI-based follow up (from tumor detection, week 0, to last time point monitored, week 7) of mice treated for 4 consecutive weeks with intrathecal injection of DMSO or Lestaurtinib 100nM. Pseudocolorized images are displayed; yellow lines outline the tumor area in MRI sections. (B) Quantitative analysis of tumor growth in follow up experiment performed as described in (A) Tumor volumes were reconstructed, summing up the corresponding voxels in each section (N = 6). Error bars, SEM. ***P<0.01; different between linear regression of each growth curve. The black arrows indicate Lestaurtinib administration. (C), Kaplan–Meier survival curves of control and mice treated for 4 weeks with Lestaurtinib at 10 weeks of age (N = 19 DMSO, 12 Lest). Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test was used to compare survival between experimental groups (*P<0,05). The black arrows indicate Lestaurtinib administration.
Pallavicini G 1,2 *, Iegiani G 1,2 *, Parolisi R 1,2 , Ferraro A 1,2 , Garello F 3 , Bitonto V 3 , Terreno E 3 , Gai M 3 and Di Cunto F 1,2 (2023) Lestaurtinib inhibits Citron kinase activity and medulloblastoma growth through induction of DNA damage, apoptosis and cytokinesis failure Front. Oncol., 19 June 2023; doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1202585
1
Neuroscience Institute Cavalieri Ottolenghi, Turin, Italy
2
Department of Neuroscience ‘Rita Levi Montalcini’, University of Turin, Turin, Italy
3
Department of Molecular Biotechnology and Health Sciences, University of Turin, Turin, Italy