Neuropharmacology
, December 2020
NPY-Y1 receptor signaling controls spatial learning and perineuronal net expression
Ilaria Bertocchi abc , Paolo Mele ab , Giuliano Ferrero a , Alessandra Oberto abc , Daniela Carulli abcd , Carola Eva abc
Perineuronal nets (PNNs) are extracellular matrix structures that form around some types of neurons at the end of critical periods, limiting neuronal plasticity. In the adult brain, PNNs play a crucial role in the regulation of learning and cognitive processes.
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is involved in the regulation of many physiological functions, including learning and memory abilities, via activation of Y1 receptors (Y1Rs).
Here we demonstrated that the conditional depletion of the gene encoding the Y1R for NPY in adult forebrain excitatory neurons (Npy1r rfb mutant mice), induces a significant slowdown in spatial learning, which is associated with a robust intensification of PNN expression and an increase in the number of c-Fos expressing cells in the cornus ammonis 1 (CA1) of the dorsal hippocampus. Importantly, the enzymatic digestion of PNNs in CA1 normalizes c-Fos activity and completely rescues learning abilities of Npy1r rfb mice.
These data highlight a previously unknown functional link between NPY-Y1R transmission and PNNs, which may play a role in the control of dorsal hippocampal excitability and related cognitive functions.
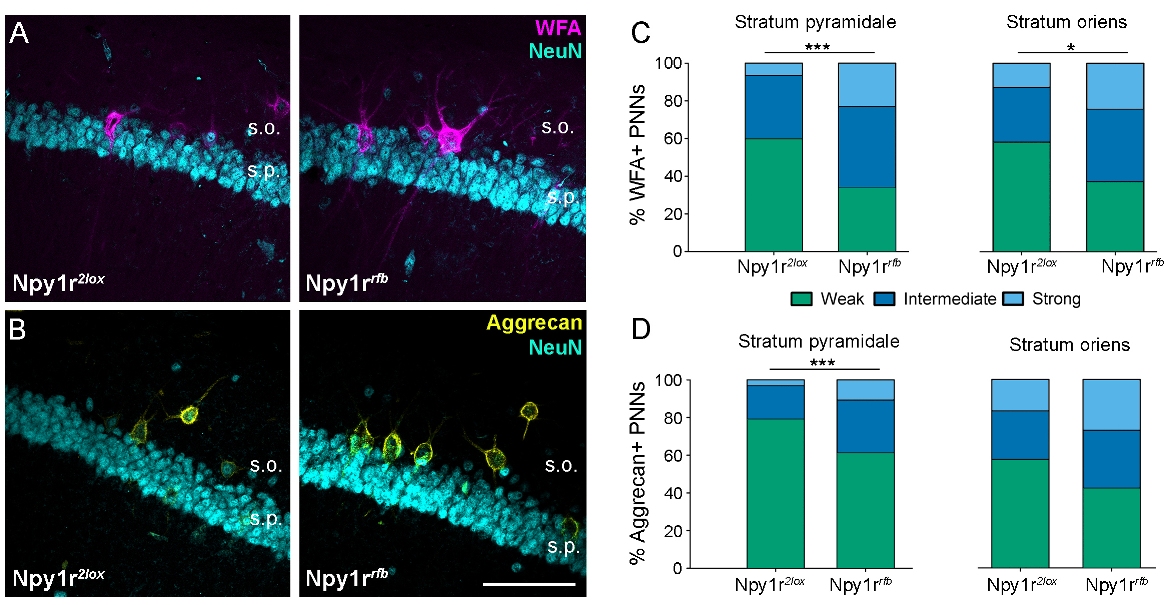
Npy1r rfb mice display increased perineuronal nets intensity in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. WFA+ (A) and aggrecan+ (B) PNNs in the in the stratum pyramidalis (s.p.) and the stratum oriens (s.o.) of the CA1 of Npy1r 2lox and Npy1r rfb mice. Scale bar: 100 μm. C and D show the frequency distribution of weak, medium or strongly stained WFA+ and aggrecan+ PNNs, respectively. ***p < 0.001; *p < 0.05. WFA, Wisteria floribunda agglutinin; NeuN, neuronal nuclear antigene.
a
Neuroscience Institute of the Cavalieri-Ottolenghi Foundation, 10043, Orbassano, Turin, Italy
b
Department of Neuroscience, University of Turin, 10126, Turin, Italy
c
Neuroscience Institute of Turin (NIT), Italy
d
Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, 1105 BA, Amsterdam, Netherlands