Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, September 2018
Pharmacological c-Jun NH(2)-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Pathway Inhibition Reduces Severity of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Disease in Mice
Roberta Schellino 1* , Marina Boido 1,2* , Tiziana Borsello 3,4 , Alessandro Vercelli 1,2
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a severe neurodegenerative disorder that occurs in early childhood. The disease is caused by the deletion/mutation of the survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1) gene resulting in progressive skeletal muscle atrophy and paralysis, due to the degeneration of spinal motor neurons (MNs). Currently, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying MN death are only partly known, although recently it has been shown that the c-Jun NH 2 -terminal kinase (JNK)-signaling pathway might be involved in the SMA pathogenesis.
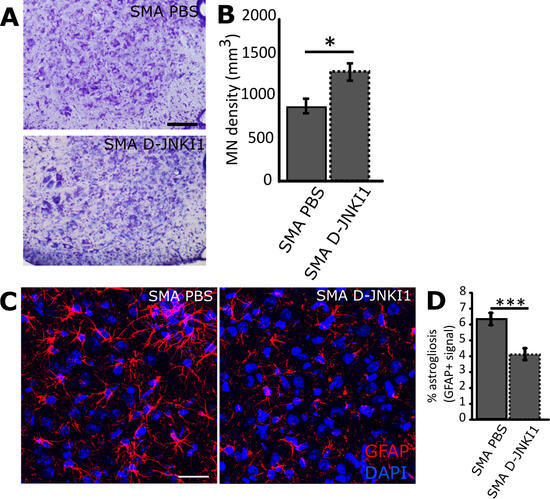
After confirming the activation of JNK in our SMA mouse model (SMN2+/+; SMNΔ7+/+; Smn−/−), we tested a specific JNK-inhibitor peptide (D-JNKI1) on these mice, by chronic administration from postnatal day 1 to 10, and histologically analyzed the spinal cord and quadriceps muscle at age P12. We observed that D-JNKI1 administration delayed MN death and decreased inflammation in spinal cord.
Moreover, the inhibition of JNK pathway improved the trophism of SMA muscular fibers and the size of the neuromuscular junctions (NMJs), leading to an ameliorated innervation of the muscles that resulted in improved motor performances and hind-limb muscular tone. Finally, D-JNKI1 treatment slightly, but significantly increased lifespan in SMA mice. Thus, our results identify JNK as a promising target to reduce MN cell death and progressive skeletal muscle atrophy, providing insight into the role of JNK-pathway for developing alternative pharmacological strategies for the treatment of SMA.
The figure shows the efficacy of D-JNKI1 administration in improving the motor neuron survival (Fig.A and B). Furthermore, the neuroinflammation (percentage of astrogliosis) is significantly reduced by the treatment (Fig. C and D).