Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences , 31 March 2021
miR-7b-3p Exerts a Dual Role After Spinal Cord Injury, by Supporting Plasticity and Neuroprotection at Cortical Level
Ghibaudi M 1,2,* , Boido M 1 , Green D 3 , Signorino E 1 , Berto GE 1 , Pourshayesteh S 1 , Singh A 4† , Di Cunto F 1 , Dalmay T 4† , Vercelli A 1
Spinal cord injury (SCI) affects 6 million people worldwide with no available treatment. Despite research advances, the inherent poor regeneration potential of the central nervous system remains a major hurdle. Small RNAs (sRNAs) 19–33 nucleotides in length are a set of non-coding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression and have emerged as key players in regulating cellular events occurring after SCI.
Here we profiled a class of sRNA known as microRNAs (miRNAs) following SCI in the cortex where the cell bodies of corticospinal motor neurons are located. We identified miR-7b-3p as a candidate target given its significant upregulation after SCI in vivo and we screened by miRWalk PTM the genes predicted to be targets of miR-7b-3p (among which we identified Wipf2 , a gene regulating neurite extension). Moreover, 16 genes, involved in neural regeneration and potential miR-7b-3p targets, were found to be downregulated in the cortex following SCI.
We also analysed miR-7b-3p function during cortical neuron development in vitro : we observed that the overexpression of miR-7b-3p was important (1) to maintain neurons in a more immature and, likely, plastic neuronal developmental phase and (2) to contrast the apoptotic pathway; however, in normal conditions it did not affect the Wipf2 expression. On the contrary, the overexpression of miR-7b-3p upon in vitro oxidative stress condition (mimicking the SCI environment) significantly reduced the expression level of Wipf2, as observed in vivo , confirming it as a direct miR-7b-3p target.
Overall, these data suggest a dual role of miR-7b-3p: (i) the induction of a more plastic neuronal condition/phase, possibly at the expense of the axon growth, (ii) the neuroprotective role exerted through the inhibition of the apoptotic cascade. Increasing the miR-7b-3p levels in case of SCI could reactivate in adult neurons silenced developmental programmes, supporting at the same time the survival of the axotomised neurons.
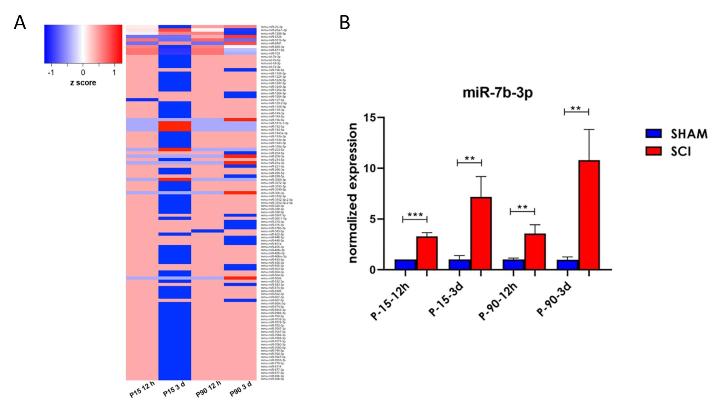
Deregulated miRNAs after spinal cord injury (SCI), represented as “heat map”, in 4 experimental groups (P15 12 ore, P15 3 giorni, P90 12 ore, P90 3 giorni).B) miR-7b-3p upregulation was confirmed in all SCI groups by real time PCR.
1
Department of Neuroscience “Rita Levi Montalcini,” Neuroscience Institute Cavalieri Ottolenghi, University of Turin, Orbassano, Italy
2
Polymers and Biomaterials, Italian Institute of Technology, Genova, Italy
3
Norwich Medical School, University of East Anglia, Norwich, United Kingdom
4
School of Biological Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, United Kingdom
Second article:
Francesca Garello, 1,† Marina Boido, 2,3,4,*† Martina Miglietti, 3 Valeria Bitonto, 1 Marco Zenzola, 1 Miriam Filippi, 1 Francesca Arena, 1,5 Lorena Consolino, 1 Matilde Ghibaudi, 2,3 and Enzo Terreno 1,* (2021) Imaging of Inflammation in Spinal Cord Injury: Novel Insights on the Usage of PFC-Based Contrast Agents . Biomedicines