Glia
, 17 June 2021
Elovl5 is required for proper action potential conduction along peripheral myelinated fibers
Eriola Hoxha* 1,2 , Ilaria Balbo 1,2 , Roberta Parolisi 1 , Roberto Spezzano 4 , Francesca Montarolo 1 , Francesco Ravera 1 , Michela Guglielmotto 1,2 , Stefania Raimondo 1,5 , Eleonora Di Gregorio 6 , Annalisa Buffo 1,2 , Alfredo Brusco 6 , Barbara Borroni 7 , Nico Mitro 4 , Donatella Caruso 4 , Filippo Tempia 1,2,3
open access article
Abstract
Elovl5 elongates fatty acids with 18 carbon atoms and in cooperation with other enzymes guarantees the normal levels of very long-chain fatty acids, which are necessary for a proper membrane structure. Action potential conduction along myelinated axons depends on structural integrity of myelin, which is maintained by a correct amount of fatty acids and a proper interaction between fatty acids and myelin proteins.
We hypothesized that in Elovl5 −/− mice, the lack of elongation of Elovl5 substrates might cause alterations of myelin structure.
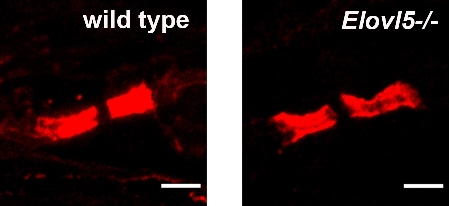
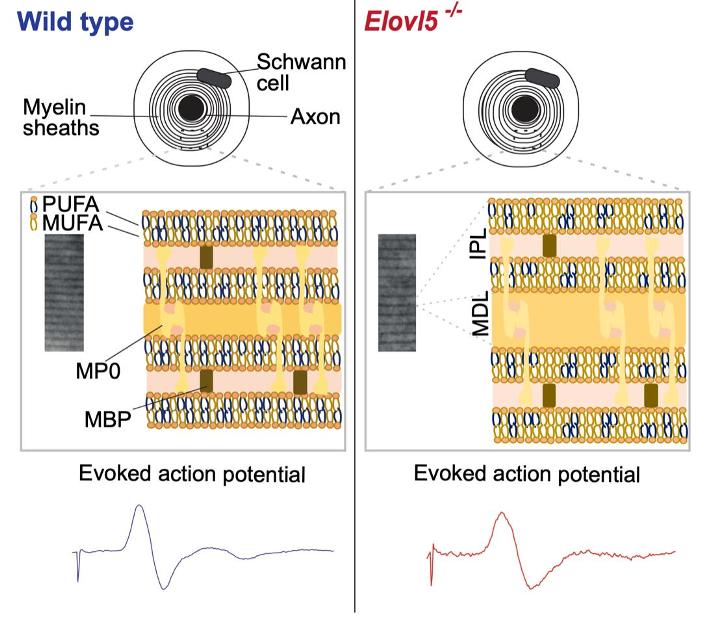
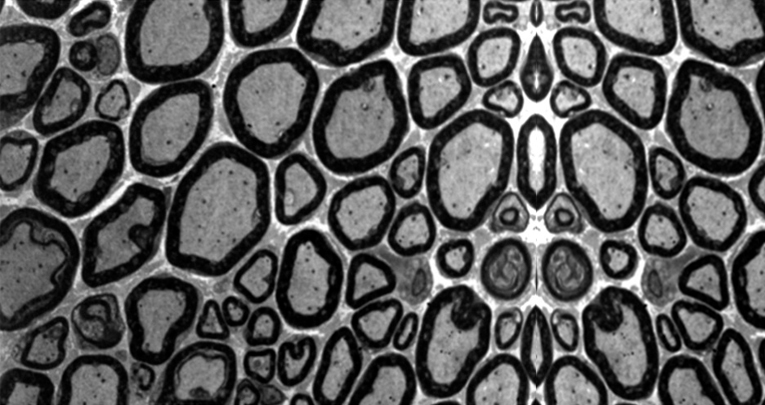
The analysis of myelin ultrastructure showed an enlarged periodicity with reduced G-ratio across all axonal diameters. We hypothesized that the structural alteration of myelin might affect the conduction of action potentials. The sciatic nerve conduction velocity was significantly reduced without change in the amplitude of the nerve compound potential, suggesting a myelin defect without a concomitant axonal degeneration.
Since Elovl5 is important in attaining normal amounts of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are the principal component of myelin, we performed a lipidomic analysis of peripheral nerves of Elovl5-deficient mice. The results revealed an unbalance, with reduction of fatty acids longer than 18 carbon atoms relative to shorter ones. In addition, the ratio of saturated to unsaturated fatty acids was strongly increased.
These findings point out the essential role of Elovl5 in the peripheral nervous system in supporting the normal structure of myelin, which is the key element for a proper conduction of electrical signals along myelinated nerves.
Loss of Elovl5 in peripheral nerves leads to an imbalance between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in membrane phospholipids, a loss of compactness of the myelin sheath, and a consequent slowing of action potential conduction.
1
Neuroscience Institute Cavalieri Ottolenghi (NICO)
2
Department of Neuroscience, University of Torino, Italy
3
National Neuroscience Institute (Italy)
4
Dept. of Pharmacological and Biomolecular Sciences, Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy
5
Department of Clinical and Biological Sciences, University of Torino, Italy
6
Medical Genetics Unit, Città della Salute e della Scienza Hospital and Dept. of Medical Sciences, University of Torino, Italy
7
Neurology Unit, Dept. Clinical and Experimental Sciences, University of Brescia, Italy