Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, June 2015
Parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synaptic impairment in a mouse model of spinocerebellar ataxia type 27
Filippo Tempia 1,2,3,4* , Eriola Hoxha 2,3 , Giulia Negro 3 , Musaad A. Alshammari 1,5,6 , Tahani K. Alshammari 1,5,6 , Neli Panova-Elektronova 1 and Fernanda Laezza 1,7,8,9*
Genetically inherited mutations in the fibroblast growth factor 14 (FGF14) gene lead to spinocerebellar ataxia type 27 (SCA27), an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by heterogeneous motor and cognitive impairments. Consistently, genetic deletion of Fgf14 in Fgf14−/− mice recapitulates salient features of the SCA27 human disease.
In vitro molecular studies in cultured neurons indicate that the FGF14F145S SCA27 allele acts as a dominant negative mutant suppressing the FGF14 wild type function and resulting in inhibition of voltage-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels.
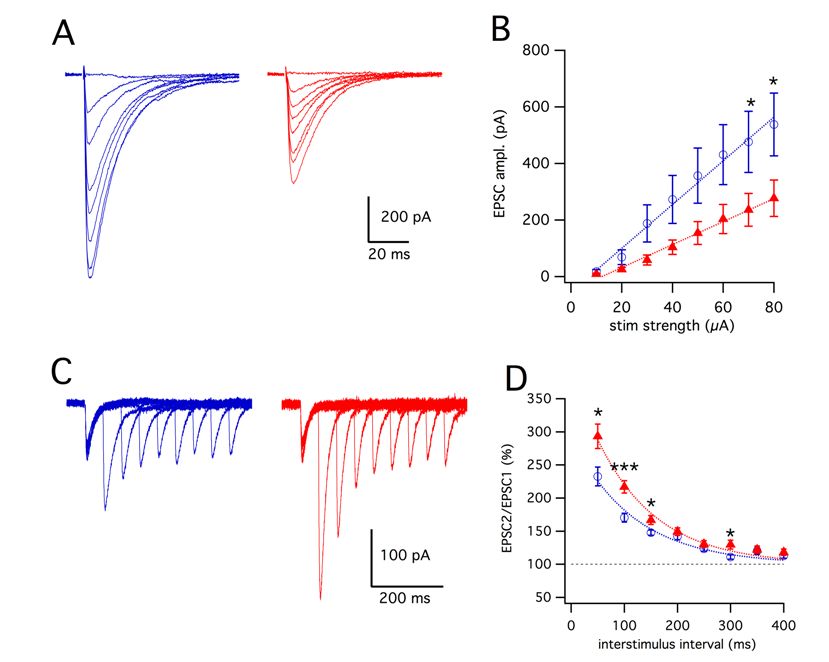
largeTo gain insights in the cerebellar deficits in the animal model of the human disease, we applied whole-cell voltage-clamp in the acute cerebellar slice preparation to examine the properties of parallel fibers (PF) to Purkinje neuron synapses in Fgf14−/− mice and wild type littermates.
We found that the AMPA receptor-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents evoked by PF stimulation (PF-EPSCs) were significantly reduced in Fgf14−/− animals, while short-term plasticity, measured as paired-pulse facilitation (PPF), was enhanced. Measuring Sr2+-induced release of quanta from stimulated synapses, we found that the size of the PF-EPSCs was unchanged, ruling out a postsynaptic deficit.
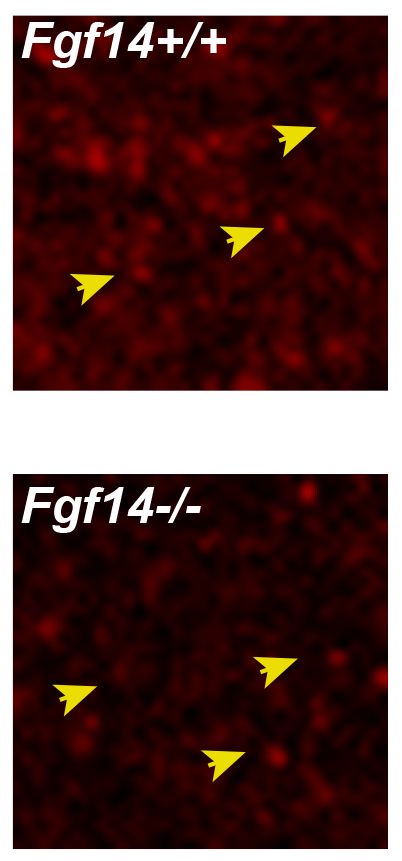
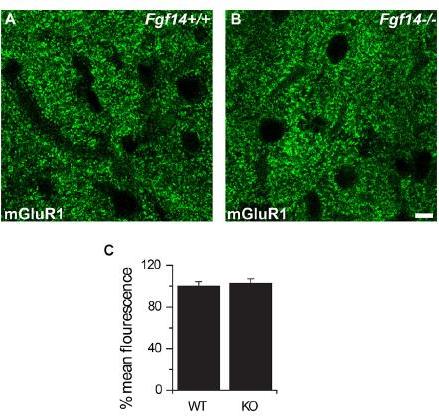
This phenotype was corroborated by decreased expression of VGLUT1, a specific presynaptic marker at PF-Purkinje neuron synapses. We next examined the mGluR1 receptor-induced response (mGluR1-EPSC) that under normal conditions requires a gradual build-up of glutamate concentration in the synaptic cleft, and found no changes in these responses in Fgf14−/− mice.
These results provide evidence of a critical role of FGF14 in maintaining presynaptic function at PF-Purkinje neuron synapses highlighting critical target mechanisms to recapitulate the complexity of the SCA27 disease.
[
read more
]